Research
The ERSL research group focuses on large-scale topology optimization, design for additive manufacturing, and high performance finite element analysis (FEA).
The novelty in the topology optimization approach is the concept of topological level-setthat combines topological sensitivity and level-set in a simple and robust manner. This has resulted in innovative methods for handling manufacturing constraints, tracing Pareto curves in multi-objective optimization, designing multi-materials and compliant mechanisms.
In parallel, the research group has made several ground breaking advances in high-performance finite element analysis. The dual-representation strategy demonstrated how classic beam and shell theories can be used as efficient preconditioners for 3D FEA. The novel concept of tangled FEAextends classic FEA to tangled meshes containing inverted elements, bypassing the unsolved problem of mesh untangling. The group also proposed the idea of limited-memory deflated FEA to exploit modern multi-core CPUs and many-core graphic programmable units (GPUs).
Research Interests
- Large-scale multi-constrained topology optimization
- Design optimization for additive manufacturing
- Additive manufacturing simulation
- High-performance (GPU/Cloud) computing
- Limited-memory finite element analysis
- Mesh generation
Current Research Projects
Topology optimization benchmark studies
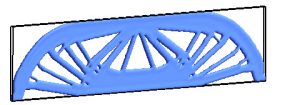
This is an effort to provide the community with topology optimized models that can be used for 3D-printing, recovery of CAD models, etc. Click here for TO benchMark models.
Limited Memory Deflated Finite Element Analysis
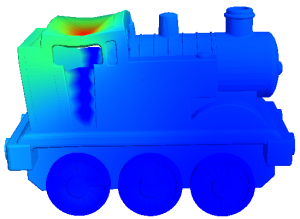
Large-scale FEA problems with millions of degrees of freedom are becoming commonplace in solid mechanics. The bottleneck in such problems is memory access. The objective of this project is to exploit assembly-free deflation techniques to accelerate FEA. Publication PDF
Large-Scale Implicit Structural Dynamics
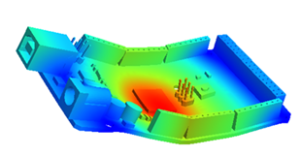
The primary computational bottle-neck in implicit structural dynamics is the repeated inversion of the underlying stiffness matrix. A fast inversion technique is proposed by combining the well-known Newmark-beta method, with assembly-free deflated conjugate gradient (AF-DCG) for large-scale problems. Publication PDF
Finite Element Analysis over a Tangled Mesh
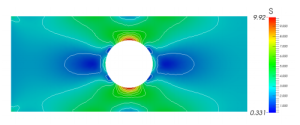
Classic FEA breaks down if one or more elements gets inverted, i.e., if the mesh gets tangled. But, mesh tangling is unavoidable during mesh generation, mesh morphing and large-scale deformation. The objective of this research is to extend classic FEA to handle tangled meshes. Publication PDF
Singularity Removal in Quad Meshes
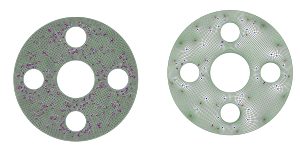
In quad meshes, nodes connected to exactly 4 quad elements are called regular; otherwise they are referred to as irregular or singular. Singular nodes are detrimental to FEA accuracy. A new singularity removal method has been developed to dramatically reduce the number of node singularities. Publication link
Topology Optimization via the Topological Level-Set
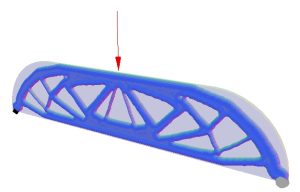
The topological level-set method developed by our group directly uses the topological sensitivity field as a level-set for an efficient solution of topology optimization problems. Publication PDF
Multi-constrained Topology Optimization
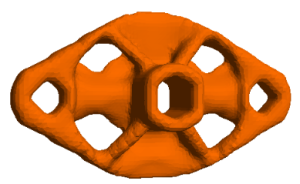
Topology optimization problems subject to several constraints are both theoretically and computationally challenging. The topological level-set method is combined here with augmented Lagrangian methods to solve such multi-constrained topology optimization problems.
Multi-material Topology Optimization
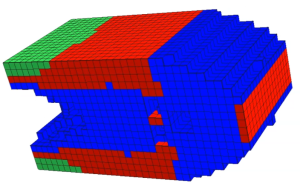
As additive manufacturing expands into multi-material, there is a demand for efficient multi-material topology optimization. The classic approach is to impose constraints on the volume-fraction of each of the material constituents. This can artificially restrict the design space. Instead, the total mass and compliance are treated as conflicting objectives, and the corresponding Pareto curve is traced; no additional constraint is imposed on the material composition. Publication PDF
Hinge-Free Compliant Mechanism Design
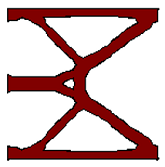
Hinges can lead to high stress concentration in compliant mechanisms. The topological sensitivity concept is exploited here to design hinge-free compliant mechanisms. These mechanisms exhibit high mechanical advantage and low stresses. Publication PDF
Topology Optimization on the Cloud
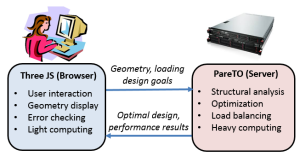
The wide-spread use of topology optimization has been deterred due to high computational cost and significant software/hardware investment. Our group has developed a cloud based implementation of topology optimization, hosted at www.cloudtopopt.com. Publication PDF
Microstructural Optimization

The objective in microstructural optimization is to find the distribution of one or more ‘materials’ that would result in a desired microscopic behaviour (ex: negative Poisson ratio). Our group has developed a highly efficient topological sensitivity based method for designing such microstructures and tracing their corresponding Hashin-Shtrikman curves. Publication PDF
Iso-Geometric Multi-material Topology Optimization
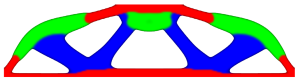
The objective here is to exploit the inherent advantages of isogeometric analysis for multi-material topology optimization. Due to the unified parametrization of geometry, analysis and design space, the sensitivities are computed analytically.
Assembly Free Additive Manufacturing (AM) Simulation
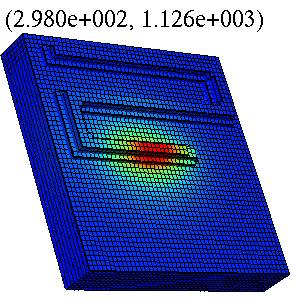
In AM simulation, repeated meshing and insertion of new elements during material deposition can pose significant implementation challenges. Our group is developing an assembly-free framework for AM simulation that offers several advantages: (1) The workspace is meshed only once at the start of the simulation, (2) addition and deletion of elements is easy since the stiffness matrix is never assembled, and (3) the underlying linear systems of equations can be solved efficiently through assembly-free deflation methods.
Software Resources
Several software modules have been created by our research group.
For example, a Matlab-based design optimization toolbox Design Optimization Software accompanies the text Design Optimization using Matlab and SolidWorks, authored by Prof. Krishnan Suresh. This module also includes SolidLab, a Matlab-based interface to SolidWorks. Also available is a Matlab-based Medial Axis Generator (Matlab) for 2D objects.
A Matlab-based design reliabiity software toobox Design Reliability Software has also been recently added.
In classic NURBS, the weights are equal along all physical coordinates. By allowing the weights to change independently in each physical coordinate, a new curve is generated which is called Generalized NURBS (GNURBS). GNURBS Lab is a MATLAB toolbox devised to generate and manipulate Generalized NURBS curves.
A unique characteristic of the research is that it has been translated into industry-strength software. For example, in 2013, the group released ParetoWorks , a topology optimization software that is integrated into SolidWorks™. It is now used by over 50+ universities around the world, and by several industrial partners. Then, in 2015, the group launched CloudTopopt, a unique cloud-based finite element analysis and topology optimization software, used by several hundred designers around the world.
As part of an outreach activitiy, we have also developed CADjs, a Javascript-based CAD programming environment. CADjs is now used both in undergraduate classes, and at local Middle and High Schools.